Abstract
Introduction: The optimal management of relapsed/refractory lymphoma is a significant clinical challenge. Early phase clinical trials are primarily designed to assess safety but also represent options for patients with limited therapeutic choices. Outcomes for lymphoma patients on early phase trials have previously been reported as single centre cohorts or grouped analyses with other malignancies. We performed a novel meta-analysis of publically available reports of early phase trials in lymphoma and compared the outcomes with those from our early phase trials unit.
Methods: The outcomes of lymphoma patients enrolled on early phase trials at a UK tertiary centre were reviewed. AEs were graded according to CTCAE v4.0 and response criteria evaluated per protocol. Patient and therapy characteristics, AEs and best clinical responses were summarised by descriptive statistics. Individual-patient survival data were analysed using Kaplan-Meier method and survival curves compared with the log-rank test. A systematic literature review was performed using EMBASE, MEDLINE and clinicaltrials.gov to identify publicly available reports of early phase clinical trials reported in 2016-2017 and data was extracted by two independent reviewers. Meta-analyses of ORRs were performed using random-effect models.
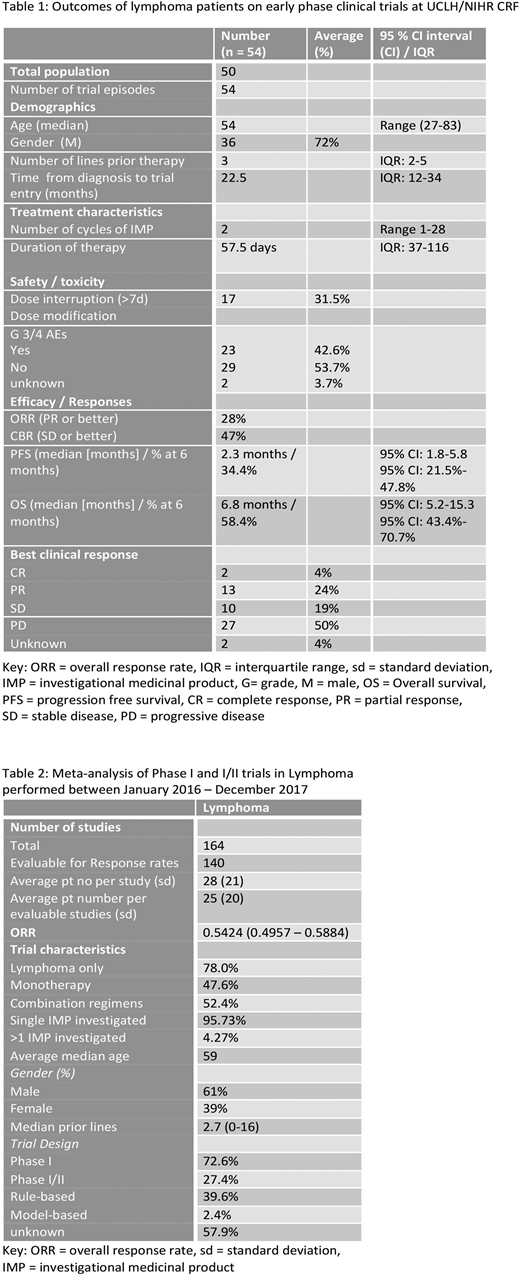
Results: 50 patients were enrolled onto 9 Phase I and I/II trials between March 2012 and June 2018, Four patients participated in 2 trials, considered separate events. 5 IMPs were small molecular inhibitors, 4 immunotherapies, 4 first in human and 8 investigated as monotherapy. Diagnoses included 42 aggressive NHL (aNHL) [30 DLBCL, 3 PMBCL, 3 Richters, 1 MCL, 5 T cell], 10 indolent NHL (5 WM, 2 FL, 2 MZL, 1 CLL/SLL) and 2 HL. Median age was 54 yr (27-83), 72% male, with a median time from diagnosis of 22.5 months and median 3 prior lines of therapy (range 1-8).
Patients received a median number of 2 cycles of IMP (range 1-28) over 57.5 days (IQR: 37-116). 42.6% experienced grade 3-4 toxicity and 31.5% required dose interruptions of >7 days. ORR and clinical benefit rate (≥SD) were 28% and 47% respectively (CR 4%, PR 24%, SD 19%). Patients were followed up for a median of 11.4 months. Median PFS and OS were 2.3 and 6.8 months respectively, with PFS and OS at 3, 6 and 12 months being 45.8%, 34.4%, 26.5% and 58.4%, 45.4% and 38.8%. Median OS was greater for those who received <4 vs ≥ 4 prior lines of treatment (9.6 vs 5.2 months, p-value log-rank test = 0.1) and those with indolent lymphoma vs aNHL (8.2 vs 6.4 months). Patients with DLBCL had a median OS of 6.8 months; ABC subtype had inferior median OS vs GC (3.4 versus 17.6 months [p-value 0.1]). Study withdrawal was due to disease progression, toxicity and allogeneic stem cell transplantation. After trial, 5.6% proceeded to SCT, 33.3% patients received other treatment, 38.9% received palliation (subsequent outcome unknown in 16.7%).
164 lymphoma trial reports were included in the meta-analysis detailing outcomes of 4537 patients (Table 2). All studies were Phase I (72.6%) or I/II and 78% included only patients with lymphoma (all other trials included reported subgroup analysis of lymphoma patients). 95.7% of trials evaluated a single IMP, 52.4% used combinations of agents. IMPs most frequently investigated were small molecule inhibitors (25.6%), antibody-drug conjugates (11.6%) and epigenetic modifiers (10.4%). Immunotherapy trials comprise 36.1% of studies, including ADCs, checkpoint inhibitors (7.32%), naked antibodies (9.2%) and cellular therapies including CAR-T (7.93%). The ORR of all patients was 54.2% (95% CI 49.6% - 58.8%). Subset analysis showed that cellular therapies studies reported a pooled ORR of 62.5% (50.9 - 72.8) and antibody therapies 58.3 (46.7 - 69.2).
Conclusion: The outcomes of lymphoma patients on early phase trials is historically perceived as very poor, partly due to the grouping of analysis with other malignancies. Our cohort had an ORR of 28% and OS at 6 months of 58.4%. The meta-analysis of global studies reporting lymphoma specific outcomes, revealed an ORR of 54.2%. This included all histological subtypes and some previously untreated patients. Our cohort was enriched for relapsed aNHL, which may account for the inferior ORR in our cohort. Together, both data sets indicate improved outcomes compared to historical reports and support enrolment of suitable patients into phase I trials when conventional options are exhausted.
Ardeshna:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Popat:Amgen: Honoraria. Townsend:Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal